Beginners Guide to Pandas and Numpy: Data Manipulation Lesson
Pandas is a python package built on Numpy and Matplotlib that is used for data manipulation and visualization. It is used by the entire python data science community. Tabular or Rectangular data is the most popular form of data for data analysis and pandas can handle its manipulation and visualization in a fluent manner. It is designed to work with rectangular data or data frames. When you first receive a dataset you want to quickly explore it and get a sense of its content. For that pandas provide several methods and attributes. At firs to import pandas in your python file following script is added at first.
import pandas as pd
Now if you have to read a CSV file using pandas then following script is used:
pd.read_csv("csv_file_location")
After you have loaded data following methods can be run in your data. Try it yourselves.
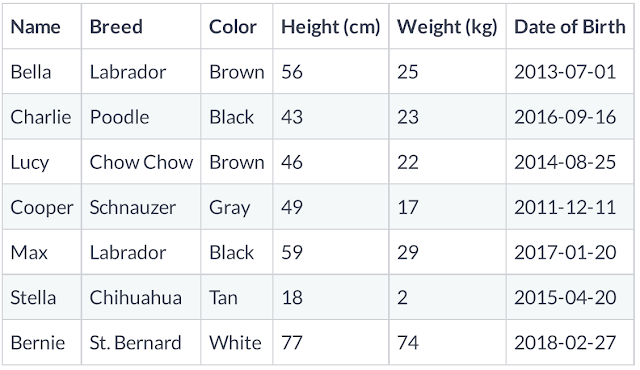
Let us consider a data frame as below and let's see what the method effects are on it.

The first is head(), it returns the first few rows of the data frames. It is very useful if we have many rows but for few rows not much difference there.
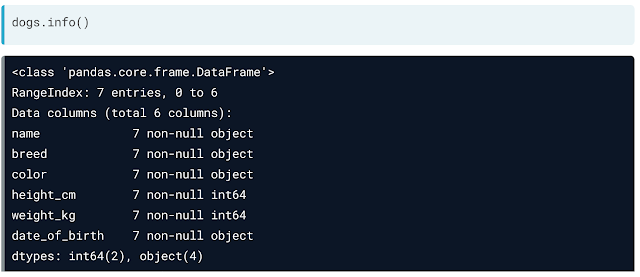
Another one is the info method. It displays the name of the column, the datatype they contain, and whether they have missing values.
Dataframe's shape is an attribute that contains a tuple that holds the number of rows followed by the number of columns. Shape is attribute not method so we write it without parenthesis.
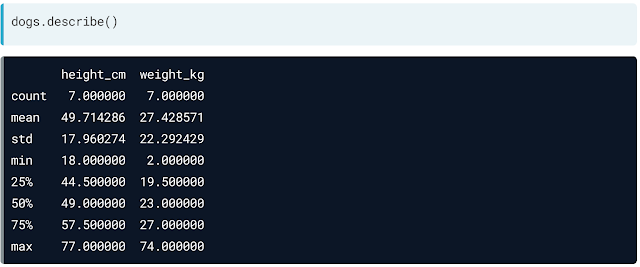
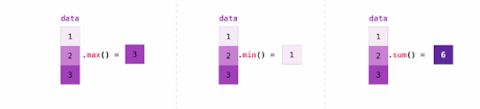
Describe is another method that computes the summary statistics for numerical columns like mean and median. It is used for a quick overview of the numeric variables. There are many summary statistics functions like median, mode, min, max, std, var, etc.
A data frame has mainly three components as Values, Index, and Columns.
Values contain the data frame values in two-dimensional NumPy array.
Index and Column return the names of rows and columns respectively. The index represents the rows and it can return numeric values.
Sorting and Subsetting
At first to sort values in the data frame according to some column we use:
dataframe_name.sort_values("name_of_column", ascending = True)
You can also the first sort by one column and then by another column as:
dataframe_name.sort_values("name_of_column", "name_of_second_column", ascending = True)
Now if you have to select certain column or columns from the whole data frame you can:
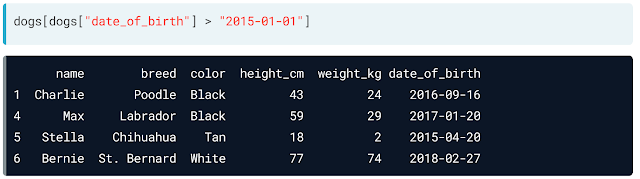
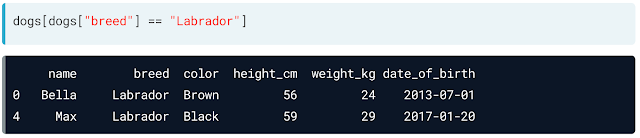
Also you can use logical operators to access certain data as:
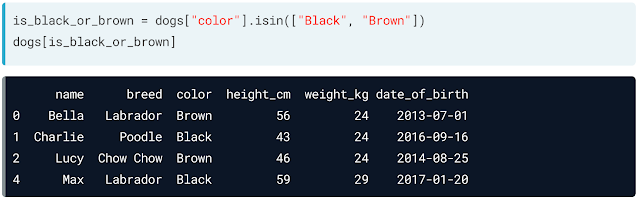
If you want to filter on multiple values of a categorical variable the easiest way is to use isin method as below:
For example, you want to add a new column to your data frame, then you can apply a method like below to add a new column. This method is also called a mutating or transforming of data frame.
There is lot more to pandas. Other topics and approaches will be added shortly.
PS: this article is based on the datacamp data science course and most of the images belong to datacamp.
Now, It's Time to Explore Numpy:
To install NumPy in your device make sure you have already installed python and pip and then:
import numpy as np
In the terminal: pip install NumPy
Now to actually use numpy in your program you first need to import it in the following ways:
Import numpy
Remember it all should be in a small letter. Whenever we use any functions from numpy we use it as below:
numpy.array
For Ease, you can import numpy as some name and use that name to call the function like below:
import numpy as np
np.array
Now lets initialize our first array first_array:
you can also initialize matrices as follow:
first_matrix = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
we can access these elements as follow:
print(a[0])\
This will print [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] for array of array.
Numpy has functions to automatically create arrays and matrices of 0's and 1's as follow:
Many functions can be performed between arrays and matrices like:
sort, concatenate, ndim, size, shape as follow:
There are also functions to reshape the size of an array as follows:
Indexing and Slicing of an array can be performed in the following ways:
Finally, I hope you are well learnt about the NumPy and pandas package and will be able to implement it in real-life situations.
Here are some of the references for you to dive deep into pandas and NumPy:





















Post a Comment